How does immersion oil work?
Optical microscopes use two basic types of objectives: dry objectives and immersion objectives. These two types of objectives differ depending on the medium between the specimen and the objective lens. In the case of dry objectives, there is no medium between the sample and the objective other than air. Immersion objectives, on the other hand, are designed to observe the sample through a layer of immersion medium that normally consists of oil. This means that just the right amount of oil needs to be placed between the coverslip that protects the specimen and the objective lens.
How does a phase contrast microscope work?
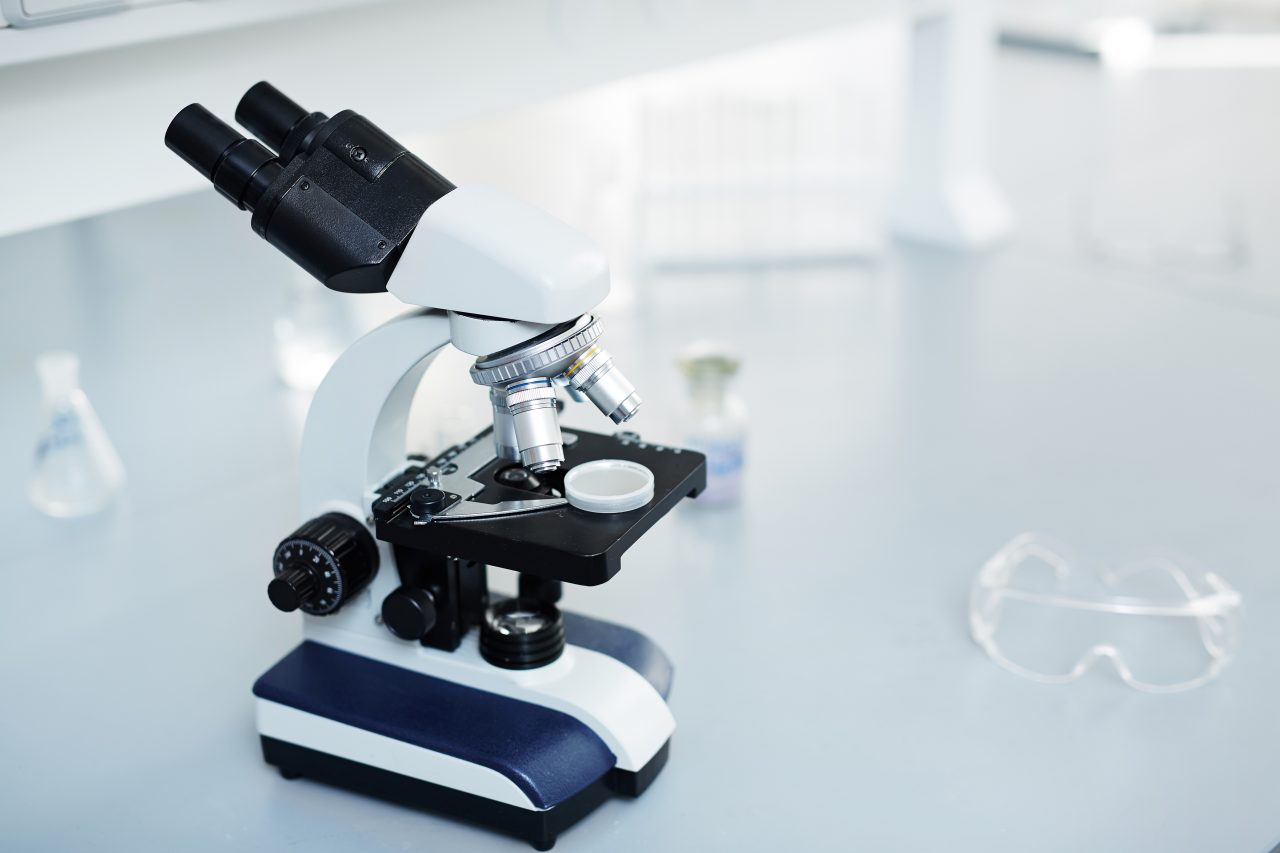

The phase contrast microscope is a type of microscope that allows you to observe live samples without using staining techniques. This microscope is based on the existence of a phase difference between the different light waves that pass through the sample to generate the image of the observation.
pHmeter: Technology and accuracy
The measurement of pH (hydrogen potential) in the laboratory is one of the most important parameters that are performed for quality control and, according to specialists in the field, it is the second most important after temperature. The determination of the pH has a great field of application: research, industry, teaching, among others. In laboratories where it is relevant to know the potential of hydrogen, a pH measuring device will always be found as a primary instrument.
Care and Calibration of your pH meter

A pH meter or pH meter is a scientific instrument that measures the activity of the hydrogen ion in aqueous solutions, indicating its degree of acidity or alkalinity expressed as pH.
The Incubators: An Ideal Atmosphere

The incubator is a device that uses various means of heat transfer and environmental control, to obtain conditions under which specialized laboratory procedures can be performed. In general, they have a system of electrical resistances that are controlled by devices such as thermostats or microprocessed controls. As for heat transfer systems, incubators basically use conduction and natural or forced convection.
What is a Laboratory Incubator?

The laboratory incubator is a piece of equipment used to maintain microbiological and cell cultures. How is this achieved? The incubator has the ability to maintain optimal temperature and humidity, as well as the levels of carbon dioxide and oxygen that may be present in the incubator.
Special Care For Your Microscope
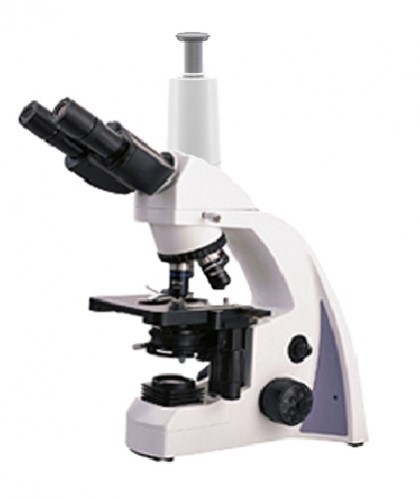

In humid climates, usually hot, microscopes are usually affected by fungi, which are formed mainly on the surface of the lens, in the screw slots and under the protective paint. If the equipment is not adequately protected, it could become unusable in the very short term. The care shown below helps prevent the formation of fungi:
Do you know what to keep in mind when using your optical microscope?
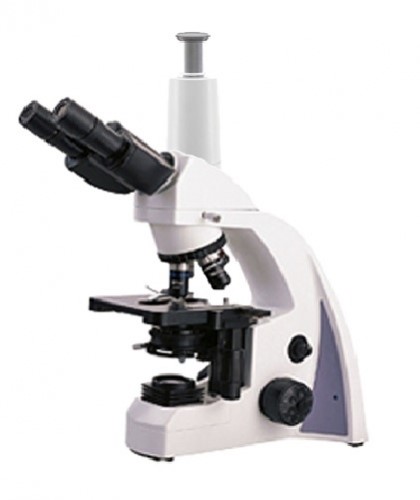

The microscope is an instrument that allows to observe objects that are not perceptible to the human eye. This is achieved through an optical system composed of lenses, which form and amplify the image of the object being observed.
Laboratory ovens, which one to choose?

Among the wide variety of equipment needed to carry out the numerous activities of a laboratory, we can highlight the use of drying and heating stoves or ovens, basic equipment that is often used quite frequently.
The drying oven: from the simple to the complex
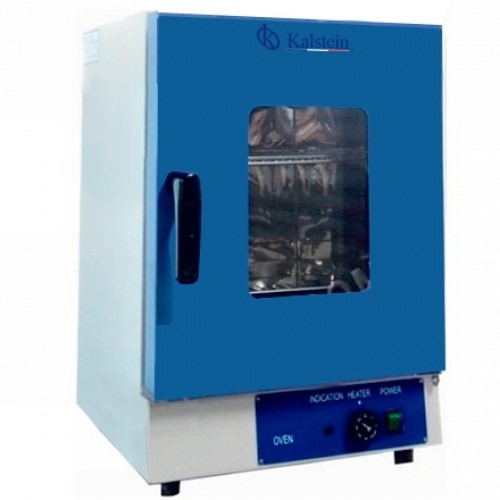

The drying oven is a device used to dry and sterilize glass and metal containers in the laboratory. It is also identified with the name Oven drying. The manufacturers have basically developed two types of stove: those that operate by natural convection and those that operate by forced convection. The stoves operate, in general, between room temperature and 350 ° C
