How is a phototherapy incubator used?

A phototherapy incubator is a specialized medical team that provides optimal conditions for the care of newborns who are not prepared for extrauterine life, and who suffer neonatal hyperbilirubinemia, clinical picture that leads to a condition known neonatal jaundice. This type of incubators have units of phototherapies, equipment composed by specialized lamps that allow to apply light therapy to treat hyperbilirubinemia, in addition to provide life support, isolate and provide heat to newborns.
Ultrasound scan: characteristics and types
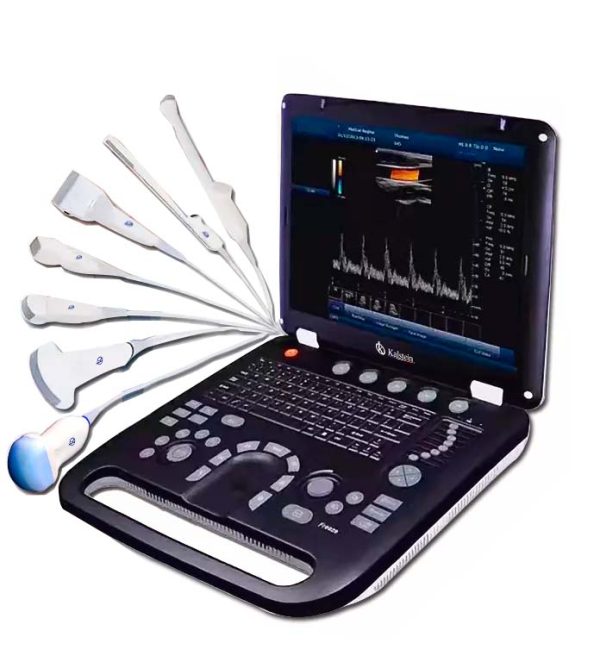
An ultrasound scanner is a medical device that allows images of most soft tissues to be obtained using ultrasonic waves. This instrument allows obtaining diagnostic images from echoes obtained by the emission of ultrasound waves (the most common).
How is an ultrasound scanner used?
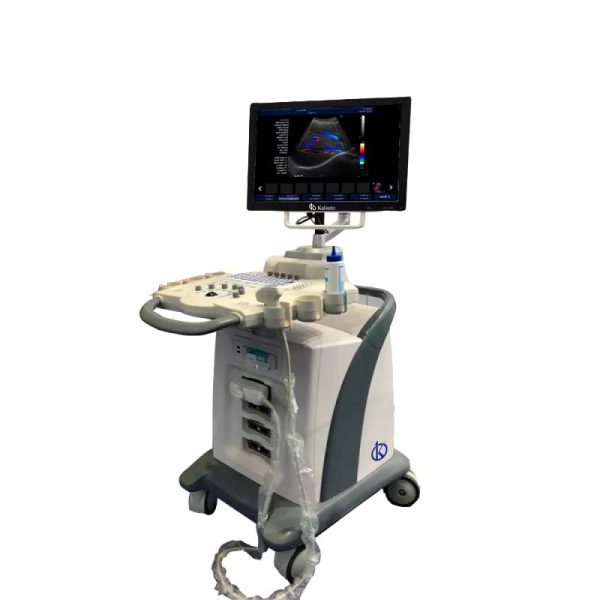
An ultrasound scanner is a specialized medical device that uses ultrasonic waves, i.e. waves with frequencies above the human ear threshold (more than 20,000 cycles per second or 20 kHz) to obtain images of most soft tissues. This instrument provides diagnostic images from the echoes obtained by the emission of these waves.
Care and maintenance of an ultrasound scanner?
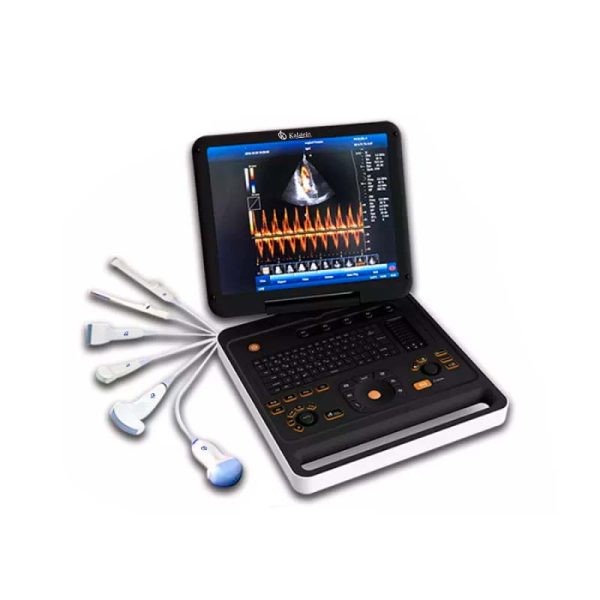
Ultrasound scanners must be maintained to be handled correctly, so care must be reasonable by inspection, sterilization or disinfection, as necessary. Failure to comply with the care and maintenance of the equipment can cause difficulties in the analysis of the same, showing undesired and erroneous results, causing irreparable damage of the equipment.
Ultrasound scan: there are risks in its use
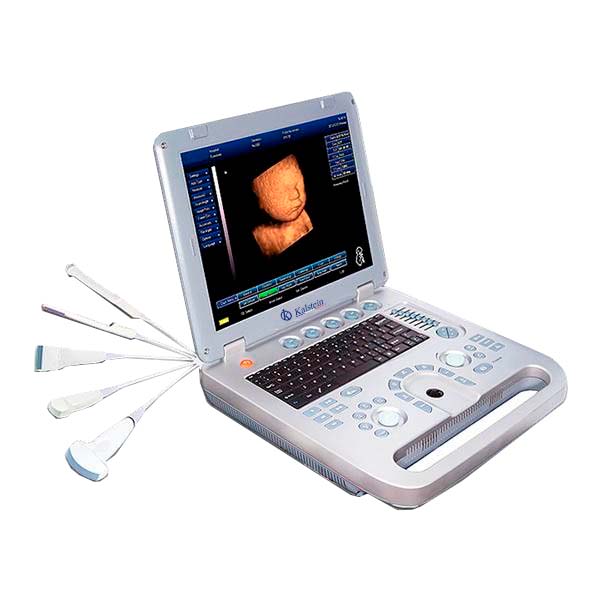
An ultrasound scanner is a medical device that uses ultrasound waves to obtain diagnostic images. These waves are generated by a device called a transducer, which in addition to producing the ultrasound waves is also able to detect the echoes reflected by the ultrasound, thus producing images of the tissues and organs.
Recommendations and ultrasound care?

An ultrasound scanner is a medical device that makes it possible to obtain diagnostic images from the echoes obtained by the emission of ultrasound waves. These waves are produced by an instrument called a transducer, which, in addition to producing ultrasound waves, is also capable of detecting the echoes reflected by the ultrasound, generating two-dimensional images of tissues and organs.
Ultrasound scanner: What data does it provide?

An ultrasound scanner is medical equipment that provides images of most soft tissues without subjecting patients to ionizing radiation. In other words, it allows obtaining diagnostic images from the echoes obtained by the emission of ultrasound waves (the most common). A small instrument called a transducer, very similar to a microphone, emits ultrasound waves. These high-frequency sound waves are transmitted to the area of the body under study and their echo is received. The transducer picks up the echo from the sound waves and a computer converts it into an image that appears on the screen.
What science do I invent ultrasound?

An ultrasound scanner is a medical device used to obtain images of most soft tissues through the use of ultrasonic waves. This device allows diagnostic images to be obtained from echoes obtained by the emission of ultrasound waves (the most common).
What is an ultrasound scanner?

An ultrasound scanner is a medical device that provides images of most soft tissues through the use of ultrasonic waves. That is, it allows obtaining diagnostic images from the echoes obtained by the emission of ultrasound waves. These waves are produced by an instrument called a transducer, which, in addition to generating the ultrasound waves, is also capable of detecting the echoes reflected by the ultrasound, generating two-dimensional images of tissues and organs.
How to know if an electrocardiogram went right or wrong?
The electrocardiogram is the test done to study the correct behavior of the heart. It is painless and very simple, offers valuable information through electrodes located in the patient’s chest, the same, are attached to the equipment, and you get 12 leads, which measure the rhythm, the regularity of the beats, the size, the position of the atria and the ventricles.
