How to remove the yellow from a baby at home?

The yellow in the skin of a newborn is called jaundice, is a condition in which he drinks has high levels of bilirubin in the blood, which is a yellow substance that the body of the newborn produces when it replaces the old red blood cells, in this process the liver intervenes, it fulfills the function of eliminating this substance through the feces of the baby, when this does not happen causes the skin and the sclera of the eyes of a baby to look yellow.
Paraffin Embedding
For the embedding of histological samples to be observed under the light microscope, paraffin is mainly used, and to a lesser extent celloidin, as embedding medium.
Chemotherapy: What type of laminar flow hoods are used?

To treat chemotherapy drugs are used that are highly dangerous, and require a series of precautions to be processed and administered, so when choosing a laminar flow hoods to prepare these medicines, we must take into account that they can cause harm to other people exposed to them, to people who handle chemotherapy drugs.
Horizontal laminar flow hoods: What is your application?

A laminar flow hoods is a laboratory equipment used to obtain a pollution-free environment, as it provides a sterile and safe area within the laboratory, and any activity that is required safely can be carried out there.
Why use an infusion pump?
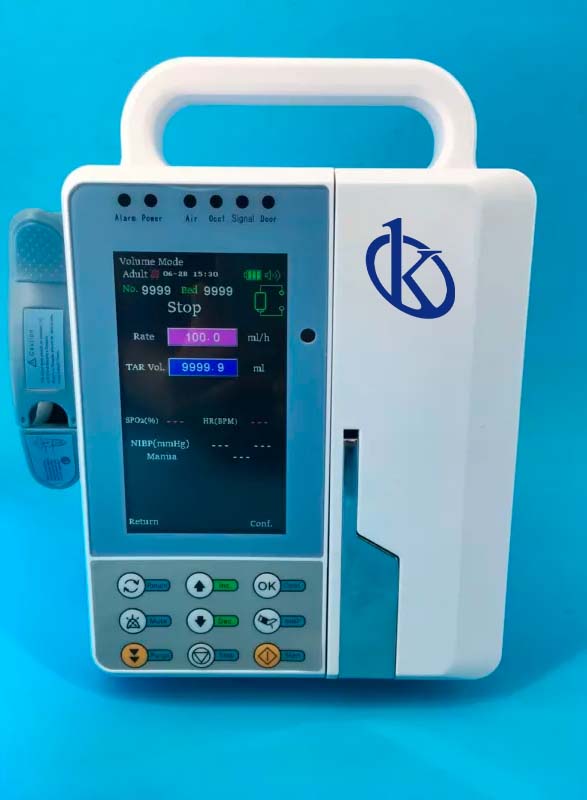
These devices are part of the medical line, they use artificial energy able to provide a positive pressure to the liquid to infuse accurately and safely in the infusion of drugs under strict flow control, one of its characteristics is that they exceed small occlusion pressures and resistance that oppose the infusion antibacterial filters and arterial lines, in addition they can infuse drugs with great precision at very low speeds.
How is an oxygen meter used?
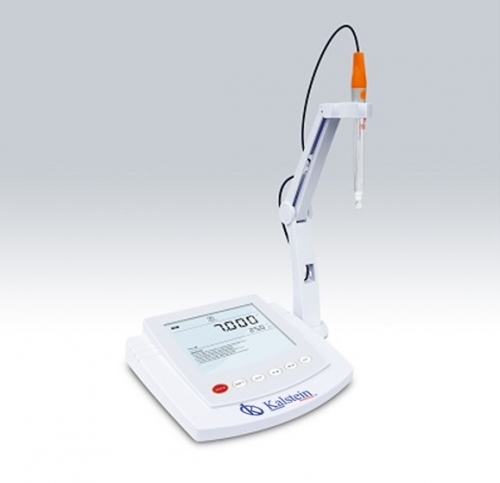
An oxygen meter is a laboratory equipment that is used to determine the amount of dissolved oxygen in liquids this uses a specialized probe that detects oxygen, this probe contains a series of optical fluorescence sensors, galvanic sensors or polarographic sensors. With this device, water can be quickly analyzed by determining the oxygen content dissolved in it.
What is an ultrasonic cleaner used for
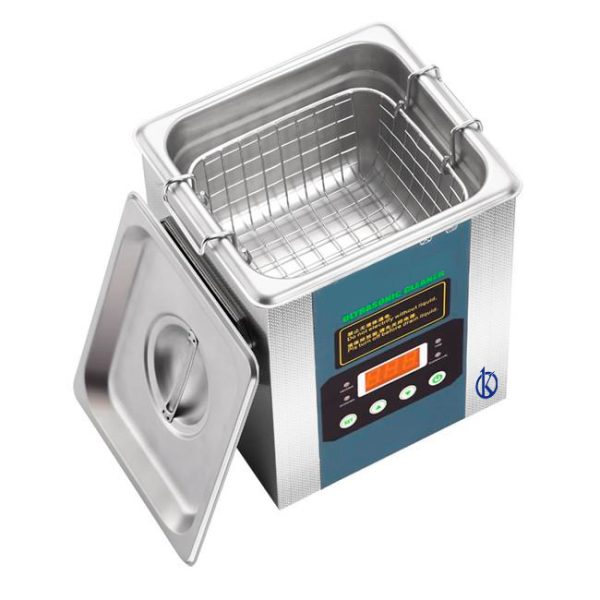

An ultrasonic cleaner is a device that effectively cleans sensitive items or hard-to-reach areas, removing dirt and bacteria that other cleaning devices fail to remove. They are usually formed by a container, in which the object or objects to be treated are introduced, immersed in a special liquid through which the high frequency waves propagate, generating an effect called acoustic cavitation through which optimal cleaning is achieved.
Conductivity meter or conductivity meter: How should he be employed?
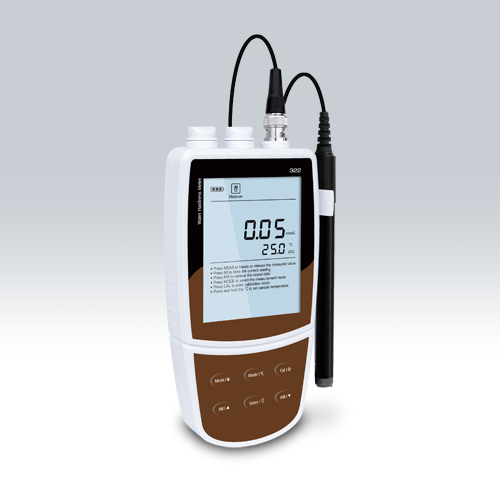

A conductivity meter or conductivity meter is a device used to determine the electrical conductivity of the ions in a solution. This is achieved because this equipment applies an electric field between two electrodes and performs a measurement of the electrical resistance in the dissolution.
What are the functions of an anesthetic machine?
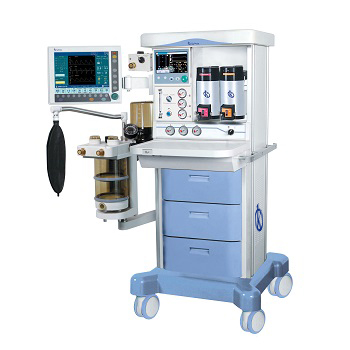
This machine is undoubtedly an indispensable equipment in health care centers, clinics and hospitals, mainly in surgical and patient recovery areas, thanks to technological advances these anesthesia machines offer safety to patients, it is used in most procedures that need to administer anesthetic gases to patients, in addition to carrying a monitored control of respiration and stable condition during the medical process.
What are the equipment used in a pathology labtech?

In a technical laboratory of pathological anatomy different services are performed that perform activities, this service has two major divisions: the area of histopathology that carries out studies of tissue samples of patients, in addition to processing and analysis of biopsies for the diagnosis of diseases or contribute to explain the symptoms of the disease; and the cytopathology area, which is in charge of the study of cytological samples, the best known is the cervical-vaginal cytology; it also includes the analysis of aspiration biopsies and any body fluid such as: pleural, peritoneal, urine, CSF, expectoration, among other samples.
