Pharmaceutical Refrigerators – Correct Temperature Range

Refrigerators are refrigeration devices used in the medical and scientific sector that are mainly intended for the preservation and storage of reagents, biological samples or medicines. In this Kalstein article, we will see that these appliances have specific characteristics that differentiate them from the refrigerators, or refrigerators, that we have in our homes, and that the functionalities, options and temperature ranges vary depending on the brands and models.
Electrophoresis Power Source
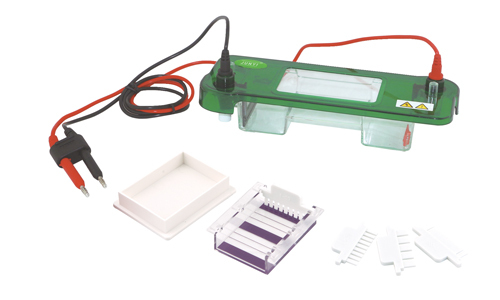
Electrophoresis is a basic method in the field of molecular biology for the analysis (separation, purification, preparation) of nucleic acids and proteins. The principle of electrophoresis consists in the migration of the molecules through a gel or another type of matrix of a porous nature, in which, by the action of an electric field, they will be separated according to their size or molecular weight, this is achieved thanks to the action of a power source for electrophoresis.
Laboratory water systems: types of waters
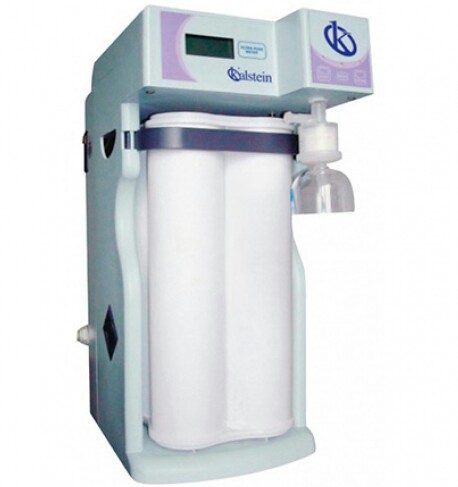

The quality of the water in the laboratory is one of the main concerns of those trying to carry out accurate and efficient experiments. The overall water purification process involves not only the final ultra-purification stage, but also a pre-treatment stage.
Cooling baths and circulation baths
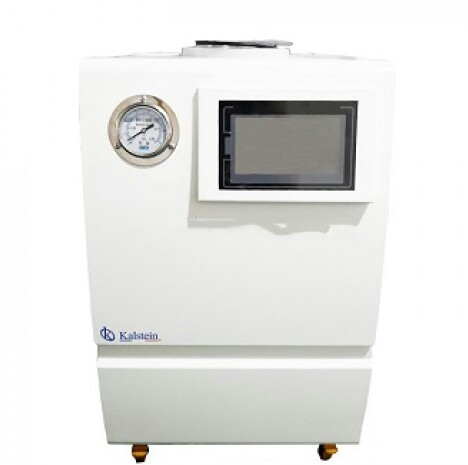

The use of cooling baths and circulation baths in research laboratories is of great importance, since both allow experiments to be carried out where the uniformity of the temperature in the sample is considered key and the objectives set by such are achieved.
What is an Ecological Microscope?
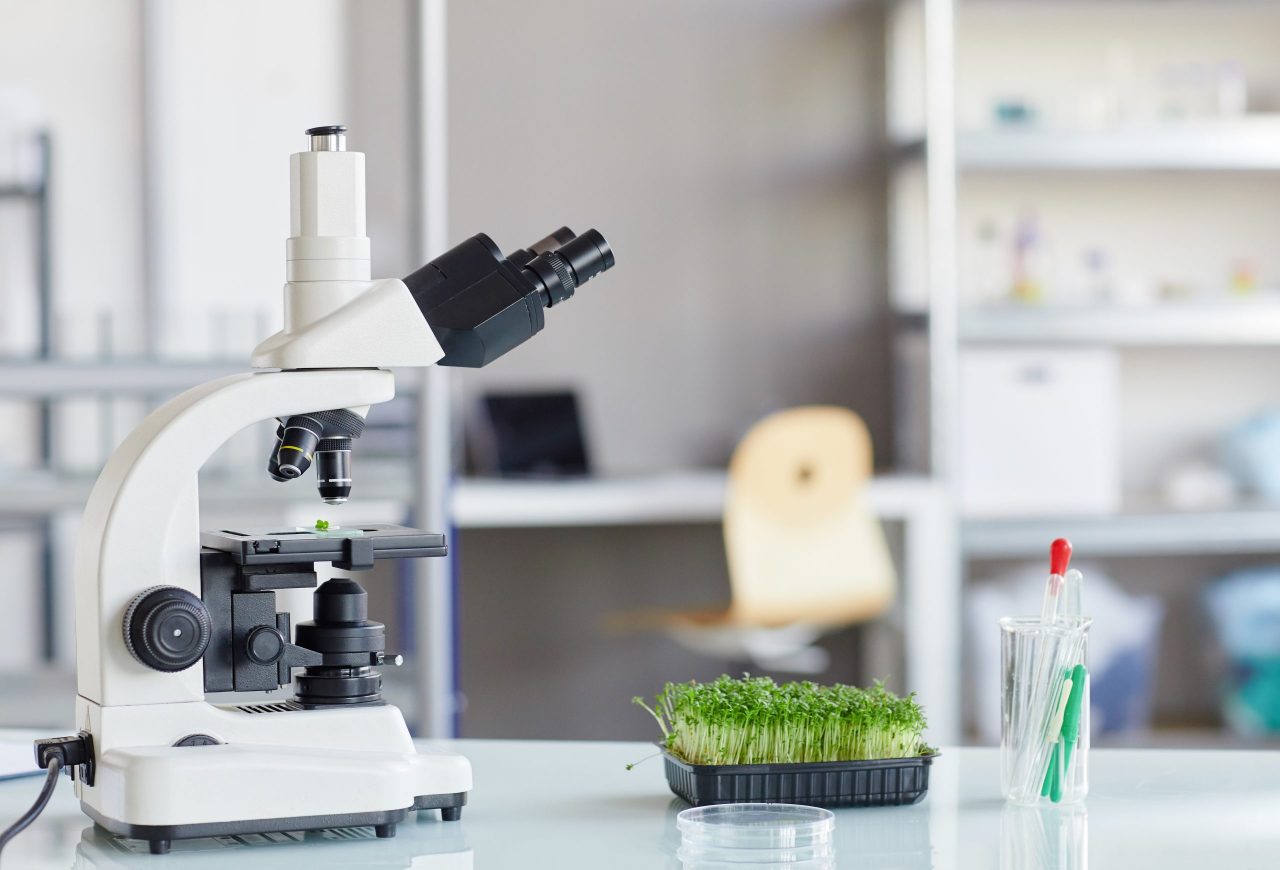

The microscope is an instrument that increases the size of an image and allows you to see more details than would be possible to see with the naked eye. There is a wide variety of microscopes, of which the ecological microscope is of relevance.
What is histopathology?

Histopathology is a branch of pathology that addresses the diagnosis of diseases through the analysis of tissues, integrating both their macroscopic and microscopic characteristics. It plays a leading role in clinical diagnosis since the analysis of the morphology of the cell allows to determine with greater precision the pathological alteration that affects the tissue and, therefore, to reach an accurate diagnosis.
What is pathological anatomy?
Pathological anatomy is the science that studies the pathophysiological and morphological alterations of the disease. It studies the disease at an organic, tissue, cellular, subcellular, and molecular level.
Electrophoresis and Gel Documentation Systems

Gel electrophoresis is a widely used technique in life science laboratories to separate macromolecules such as DNA, RNA, and proteins. In this technique, molecules are separated according to size and electrical charge.
What is a cryostat?
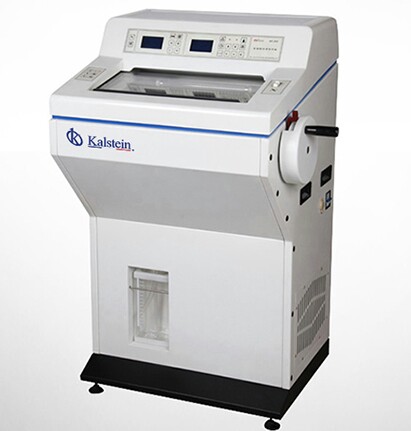

The cryostat is a piece of equipment used in the processing of samples for histological or histopathological diagnosis or identification. It is mainly used to freeze and obtain frozen tissue sections or samples that have not been previously fixed by chemical methods, to avoid losing some important characteristics necessary for observation.
Main applications of a CO2 incubator
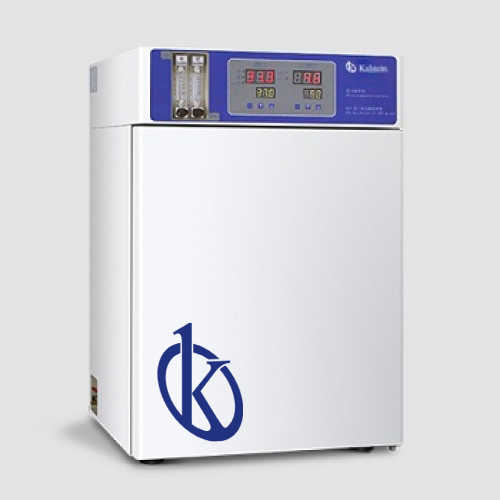

A CO2 incubator is a laboratory equipment also called a gasification incubator, where the development of cell and tissue cultures is guaranteed by creating a natural atmosphere. This culture of living organisms in vitro is one of the main applications of CO2 incubators. That is why these devices are used mainly in medical research and in the pharmaceutical industry in:
