Double door autoclave: Application

Double door autoclaves are a special type of autoclave used in clean rooms and containment suites. In the case of a clean room application, the autoclave is used for the sterilization of equipment entering a clean or aseptic area, such as a pharmaceutical production environment.
The microtome and bone cutting
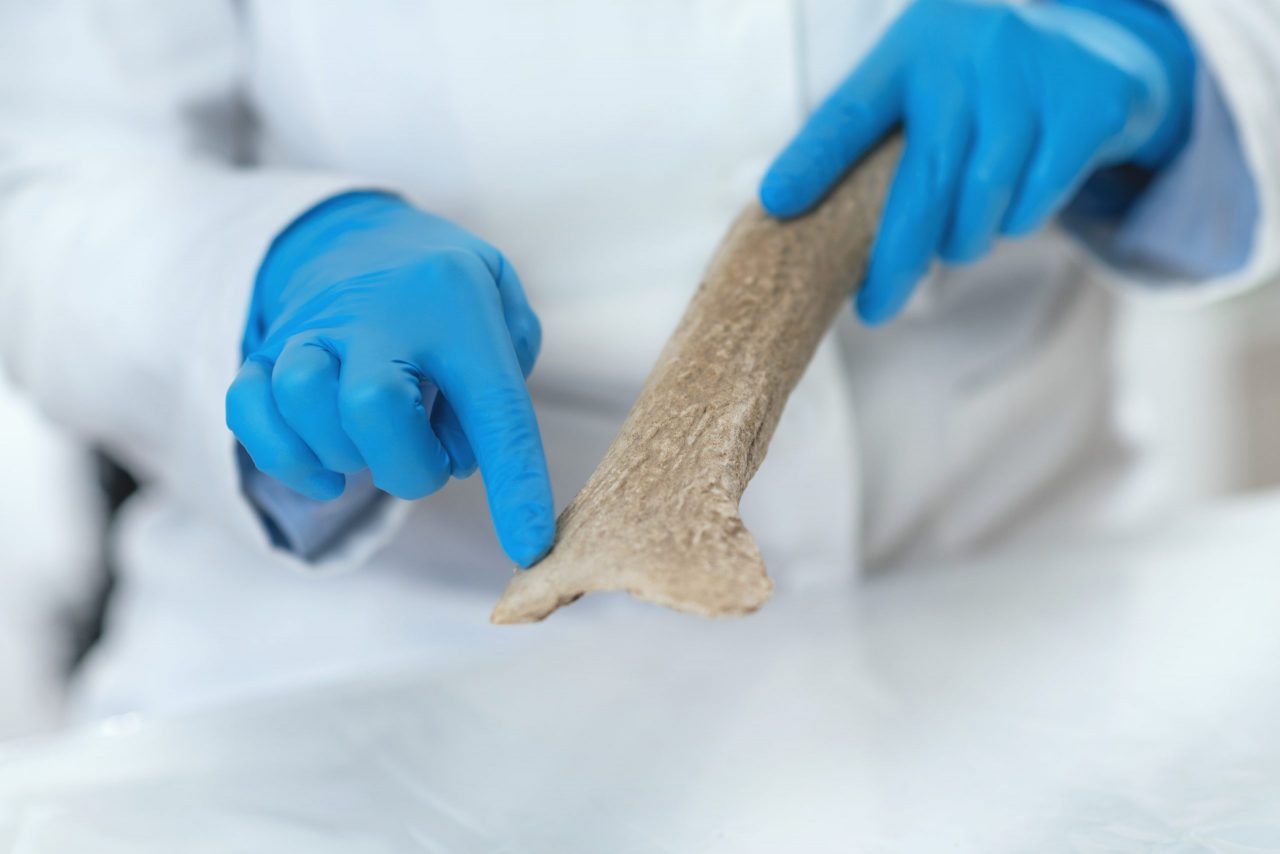

The microtome is a mechanical instrument used to cut biological samples into very thin segments for microscopic examination. Biological samples can be embedded and presented in many ways for sectioning. But more often, these samples are embedded in paraffin wax blocks and the most common way to section these samples is by microtome.
Types of laboratory ovens
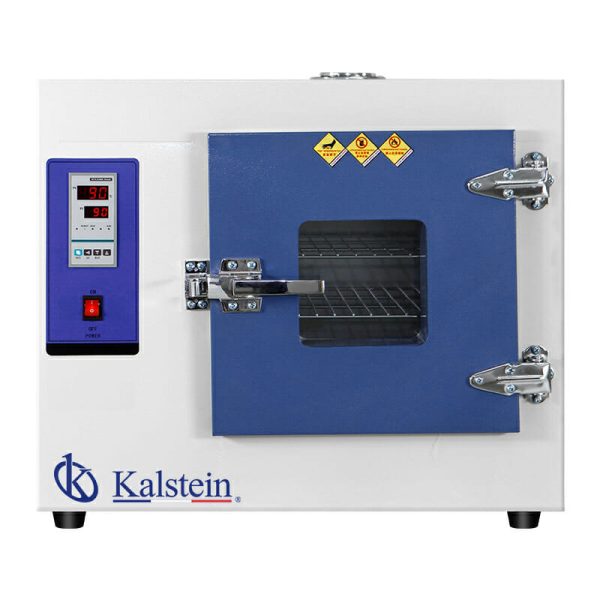

The laboratory stoves or drying oven is equipment used to dry and sterilize glass and metal containers in a laboratory. It is also known as a drying oven. They work between room temperature and 350 ° C. In general, these equipments are made of stainless steel, both inside and outside, this provides them with high durability. In addition, they have a microprocessor that makes sure to maintain a uniform temperature and allows it to be set digitally.
Refrigerator Role: COVID-19 Vaccine Storage
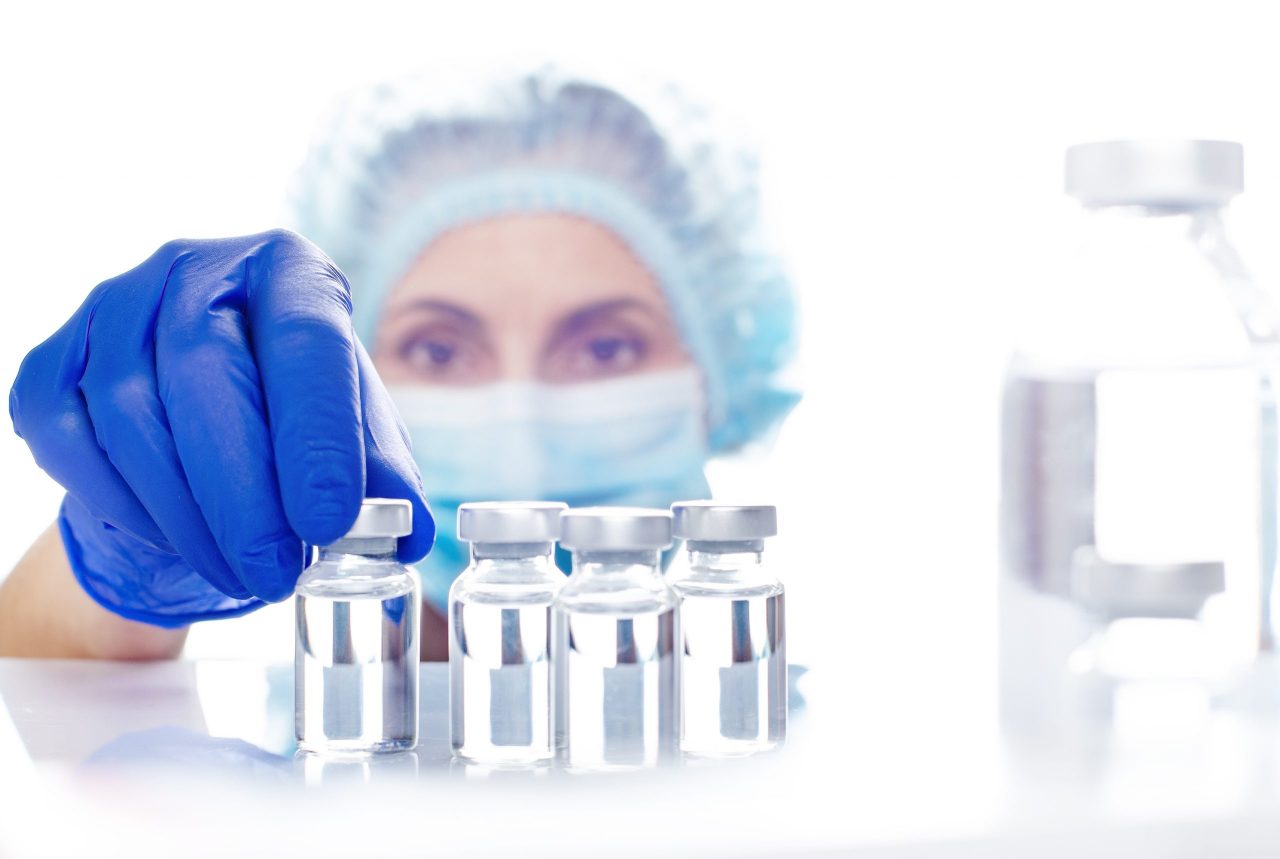

A medical product of great importance and especially sensitive to the health emergency caused by COVID-19, are vaccines. Correct cooling makes a difference and can save lives. But why is where and how vaccines are stored so important? In this article we will define what the cold chain is and what are the fundamental differences between a scientific refrigerator and a domestic refrigerator.
How does a clinical chemistry analyzer work?
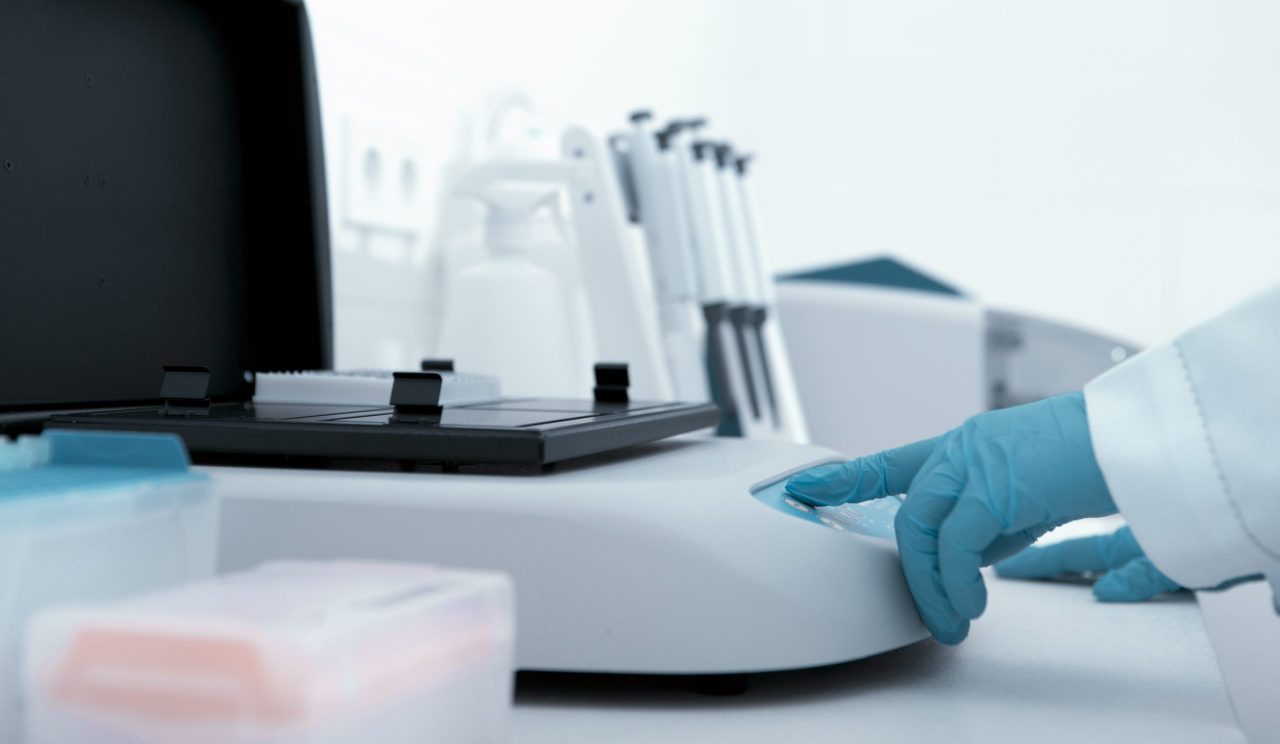
Clinical chemistry analyzers are instruments that test clinical samples such as blood serum, plasma, urine, and cerebrospinal fluid to detect the presence of disease- or drug-related analytes. Clinical chemistry analyzers are used in a variety of settings, including small clinics, research labs, and high-throughput hospital labs.
What is a laboratory oven for?
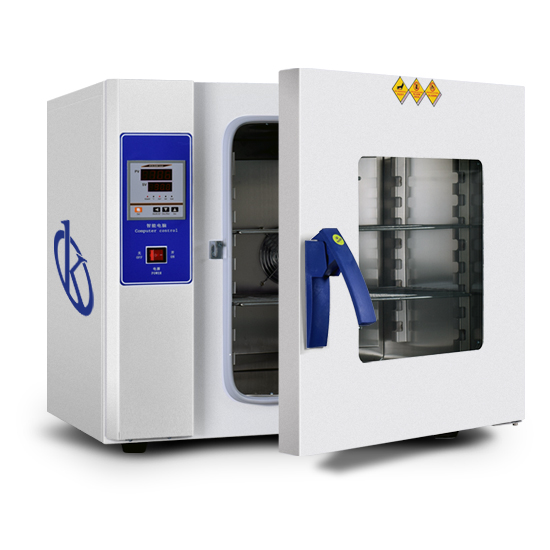

The laboratory oven is an instrument used to dry and sterilize glass containers, which come from a laboratory wash. In other words, this cavity chamber, which will have a higher temperature than the ambient temperature, will remove all the moisture from the metal or glass container.
What is a hematocrit centrifuge?
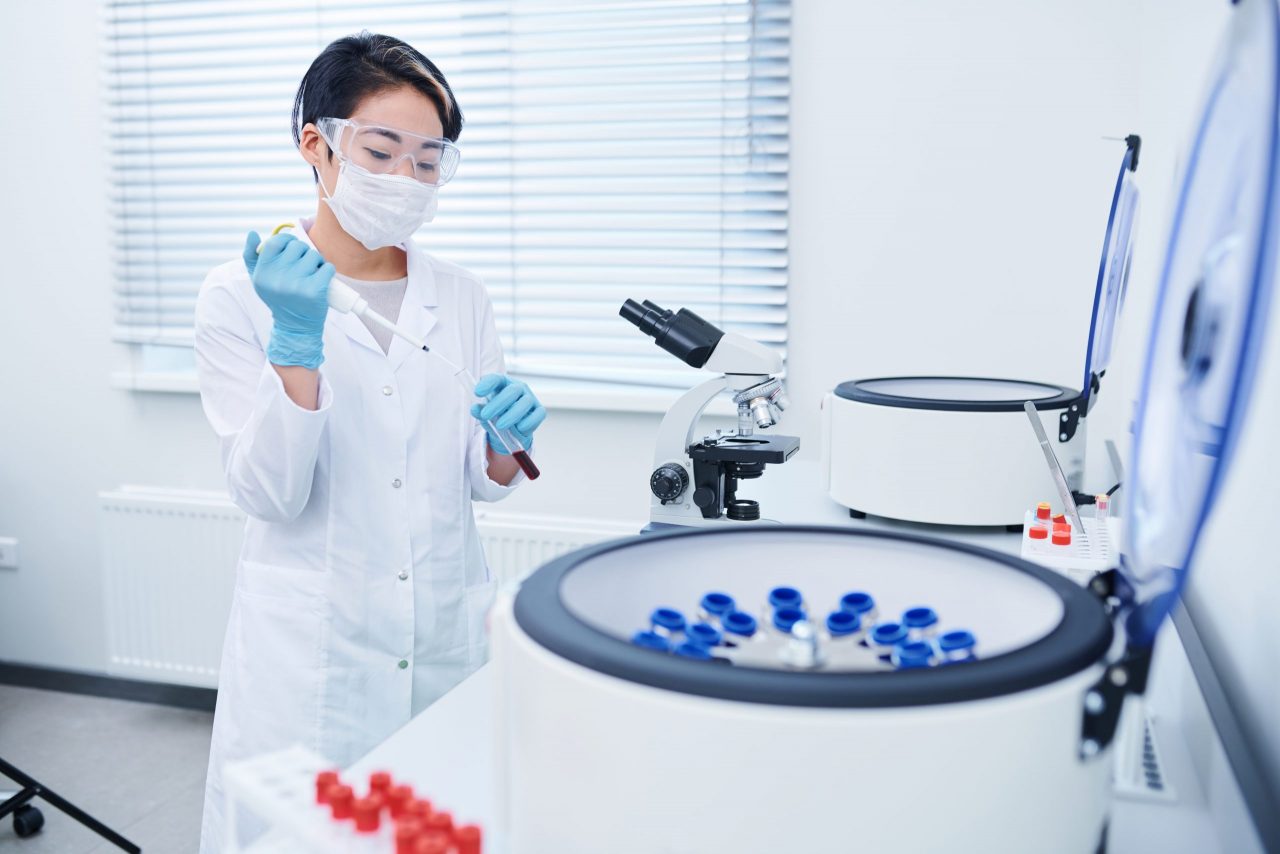

A centrifuge for hematocrit is specialized equipment that allows to obtain the compact ratio of the volume of erythrocytes in the blood. In less than seven minutes, this machine allows the erythrocytes to reach their maximum compaction density, thus knowing their hematocrit level and also having cell-free plasma used later in other analyzes.
What is a centrifuge?
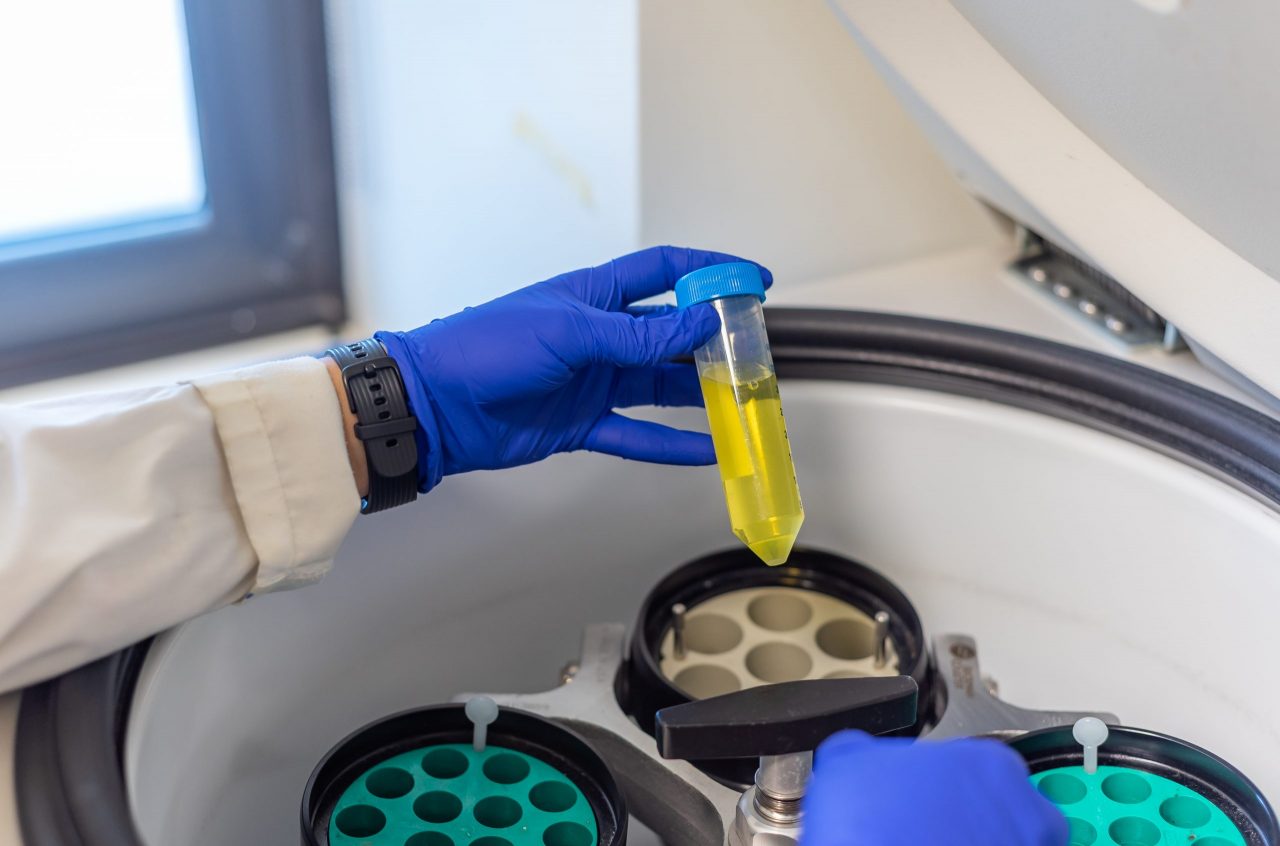

Centrifugation is a mechanism for separating mixtures (in particular, those made up of solids and liquids of different densities) through their exposure to a rotating force of a certain intensity. Centrifugal force causes objects to move away from the center as they rotate. It is the same used by a centrifuge, an instrument capable of generating centrifugal force, to separate mixtures in a laboratory.
The Microscope and its evolution
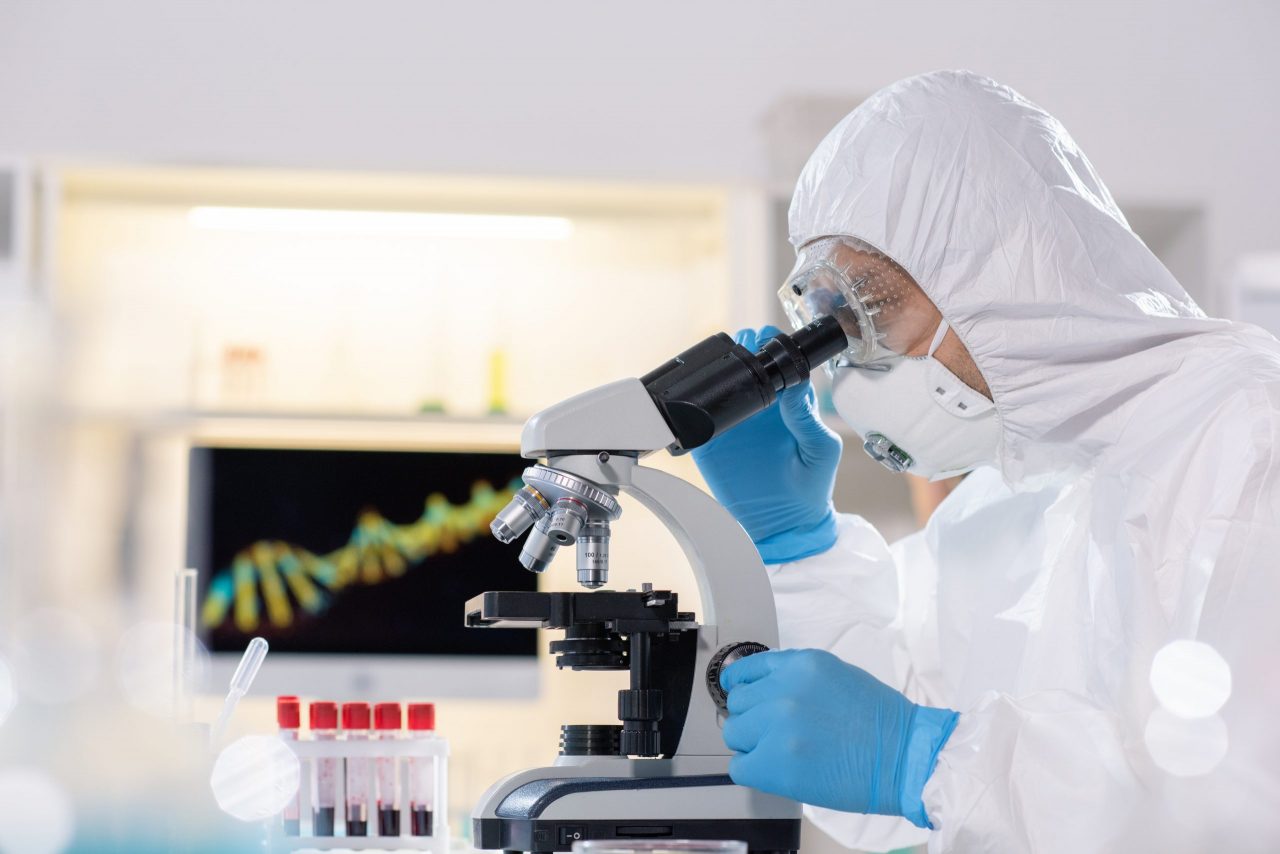

The first great advances in science and in particular in the biological sciences are due in part to the invention of the optical microscope, when at the end of the seventeenth century Anton van Leeuwenhoek, carving lenses, was able to appreciate the world that due to its small size was impossible see with the naked eye: the microscopic world.
pH meter vs. dissolved oxygen meter
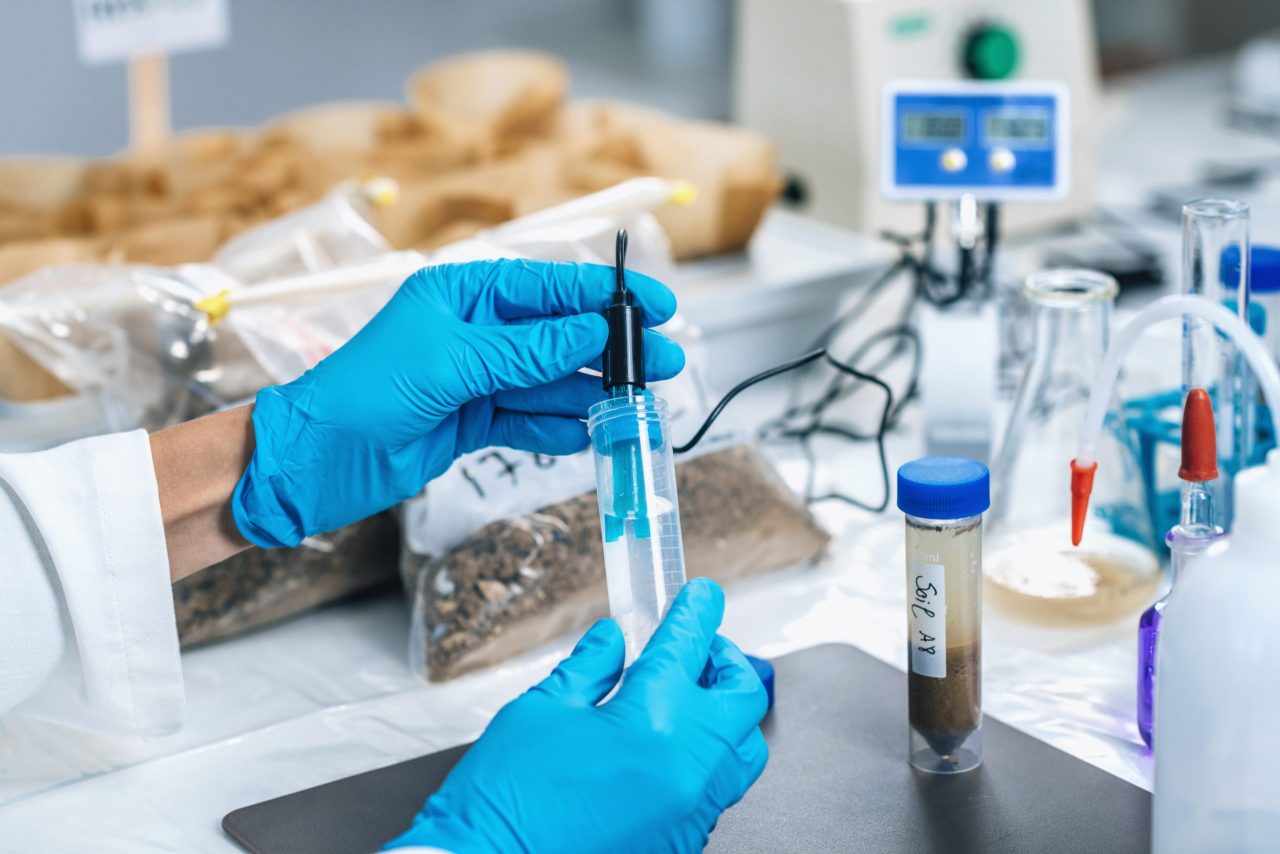

The pH is the unit of measurement that describes the degree of acidity or alkalinity and is measured on a scale ranging from 0 to 14. An approximate indication of pH can be obtained using pH indicators or tapes, which change color depending on the variation of the pH level. But these indicators have limitations in terms of accuracy and can be difficult to interpret correctly in dark or colorful samples.
