What applications do refrigerators have in the healthcare sector?

The refrigerator is an equipment whose function is to maintain, in a controlled environment (refrigerated space), various fluids and substances, so that they are kept in good condition. The lower the temperature, the less chemical and biological activity.
Two main types of refrigerators are distinguished in the health sector: laboratory refrigerators and pharmacy refrigerators. Both must allow easy and complete cleaning of surfaces and must offer high reliability, especially with regard to temperature control. Some models also offer an automatic defrost and / or forced air cooling function.
How does an autoclave work?

Moist heat destroys microorganisms by coagulation of their cellular proteins. The main sterilization method using moist heat is pressure steam sterilization. There are also other decontamination methods that use this type of heat which, although they do not allow the total destruction of microorganisms, reduce the microbial load of a material.
Tissue processing for histological studies

issue processing is a very important part of any histology laboratory, and begins with obtaining the tissue under study. In the case of plant tissues, samples of the different organs that make up the body of the plant are taken directly, while human and animal tissues can be obtained in different ways through biopsies (excisional, incisional, endoscopic, colposcopic, etc. .) and by autopsy / autopsy.
Tissue water bath

Water baths are a very common element in any type of microbiological laboratory. This type of equipment is a container that is able to retain hot water to incubate samples in water at a constant temperature for a prolonged period. Water baths generally have an interface that allows the user to set the correct temperature to achieve the desired results.
The hematological analyzer: A great medical innovation
The knowledge about the pathophysiological changes that accompany the health-disease process reached by the medical sciences during the second half of the 20th century was vertiginous. This translated for the clinical laboratory branch, in the emergence and placement in the hands of its professionals, of an increasing number of determinations aimed at complementing the physical examination and medical interrogation, to finally establish a diagnosis.
How to choose the right biochemical analyzer?

A biochemical analyzer is a laboratory equipment, which has among its functions to measure the level in blood or other body fluid, of analytes such as glucose, cholesterol, triglycerides, uric acid, proteins and enzymes.
What should I do when there is a spill in my analyzer?
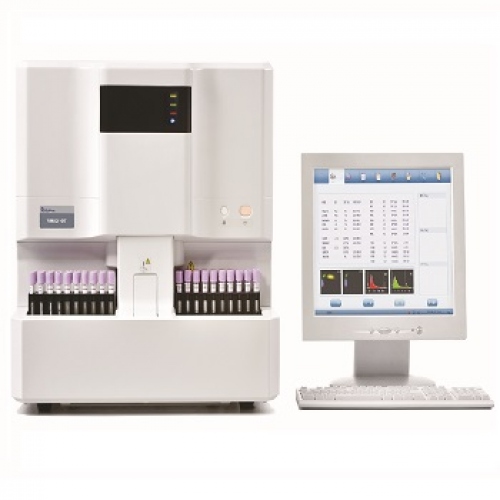

Semi-automated chemistry analyzers, in general, are very specialized and expensive equipment. Its conservation depends largely on the way of installation and use. This team is one of the main diagnostic and research instruments developed by humans. It is used in the laboratory in order to determine the concentration of a substance in a solution, thus allowing quantitative analysis.
What is a Spectrophotometer?
A spectrophotometer is a device that is used in laboratories to determine what the beam of electromagnetic radiation or light is and thus identify, qualify and quantify its intensity.
In the same way, it allows determining its efficiency, sensitivity, resolution and spectral range. Which will depend on the variabilities of the design and the choice of the optical components it contains.
What is a laboratory incubator?
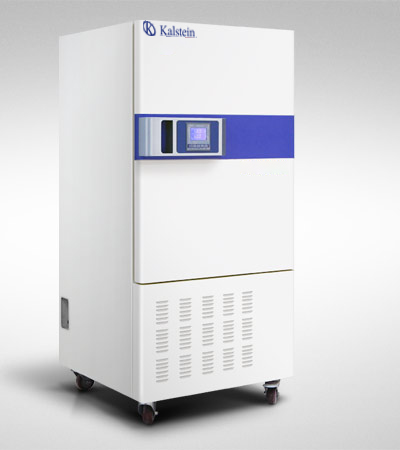

The laboratory incubator is a piece of equipment used to maintain microbiological and cell cultures. How is this achieved? The incubator has the ability to maintain optimal temperature and humidity, as well as the levels of carbon dioxide and oxygen that may be present in the incubator.
How does a fume hood work?
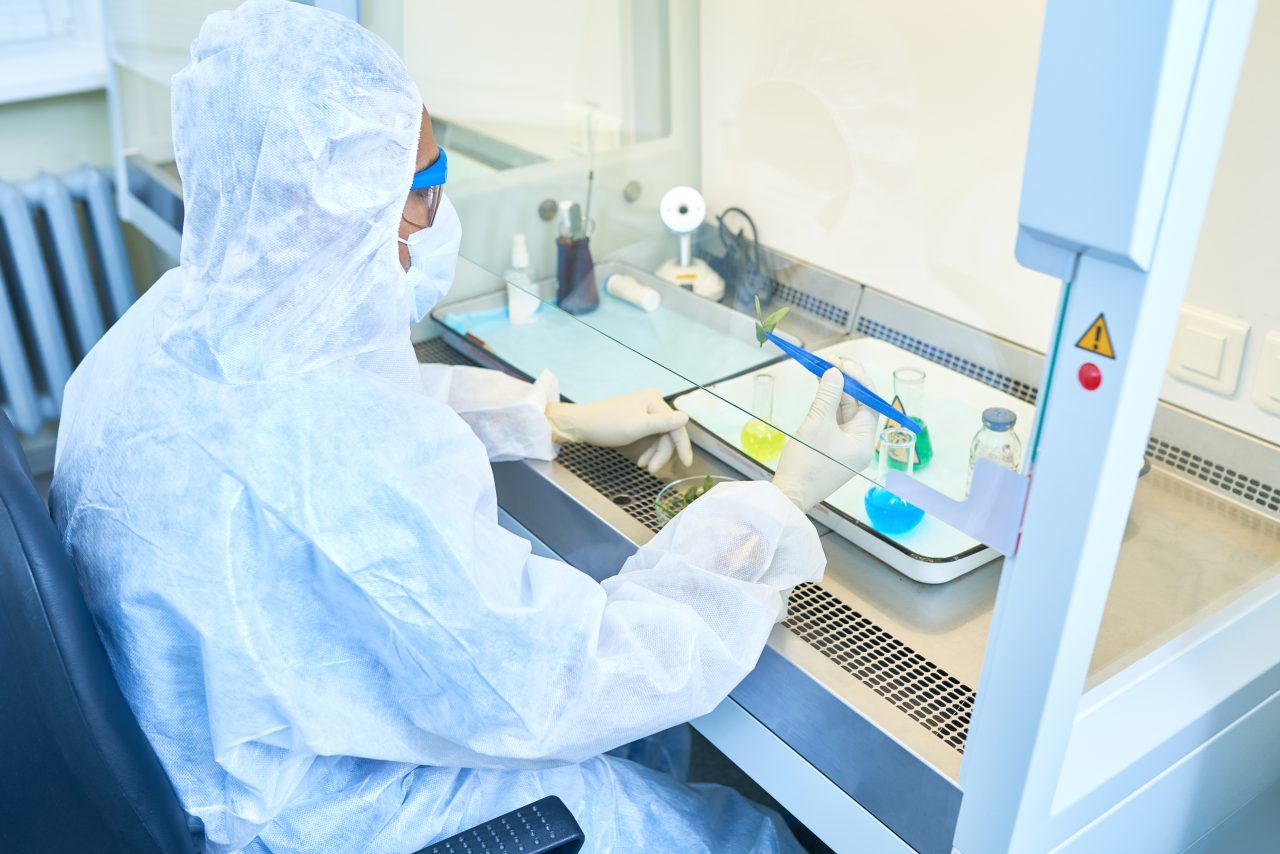

A hood or hood in laboratories are an effective means of capturing flammable, irritant, corrosive, carcinogenic vapors, etc. to prevent personnel exposures and avoid their dissemination in the laboratory atmosphere. When the hatch is down, the cab is also a physical barrier that protects the operator from hazards such as splashes, aerosols, fires, and minor explosions.
