Enhancing Post-Surgical Recovery: A Look at Kalstein’s Veterinary Rehabilitation Equipment

Over the past few years, veterinary rehabilitation has become an essential part of pet recovery following any form of surgery or injury. Kalstein veterinary rehabilitation teams are revolutionary tools that have transformed this field, offering veterinarians advanced treatment techniques that were previously only available to humans.
Optimizing Healthcare: Patient and Infant Monitors from Kalstein

In our dynamic and ever-evolving world, high-quality laboratory equipment is a non-negotiable necessity. Nowhere is this reality more evident than in the sphere of healthcare. In this arena, patient monitors and infant monitors stand out as an invaluable investment for long-term health and well-being. As a leading manufacturer, Kalstein understands this need and provides highly efficient and reliable equipment.
Transforming Animal Health: A Look at Kalstein Veterinary Surgical Equipment

In the competitive realm of veterinary medicine, professionals require the most advanced and high-quality systems to ensure effective animal care. As a leading manufacturer of veterinary surgical equipment, Kalstein has brought its commitment to innovation and quality to this important field.
Competitive Advantages of Kalstein Veterinary Surgical Teams: Leading Manufacturer in Quality and Price
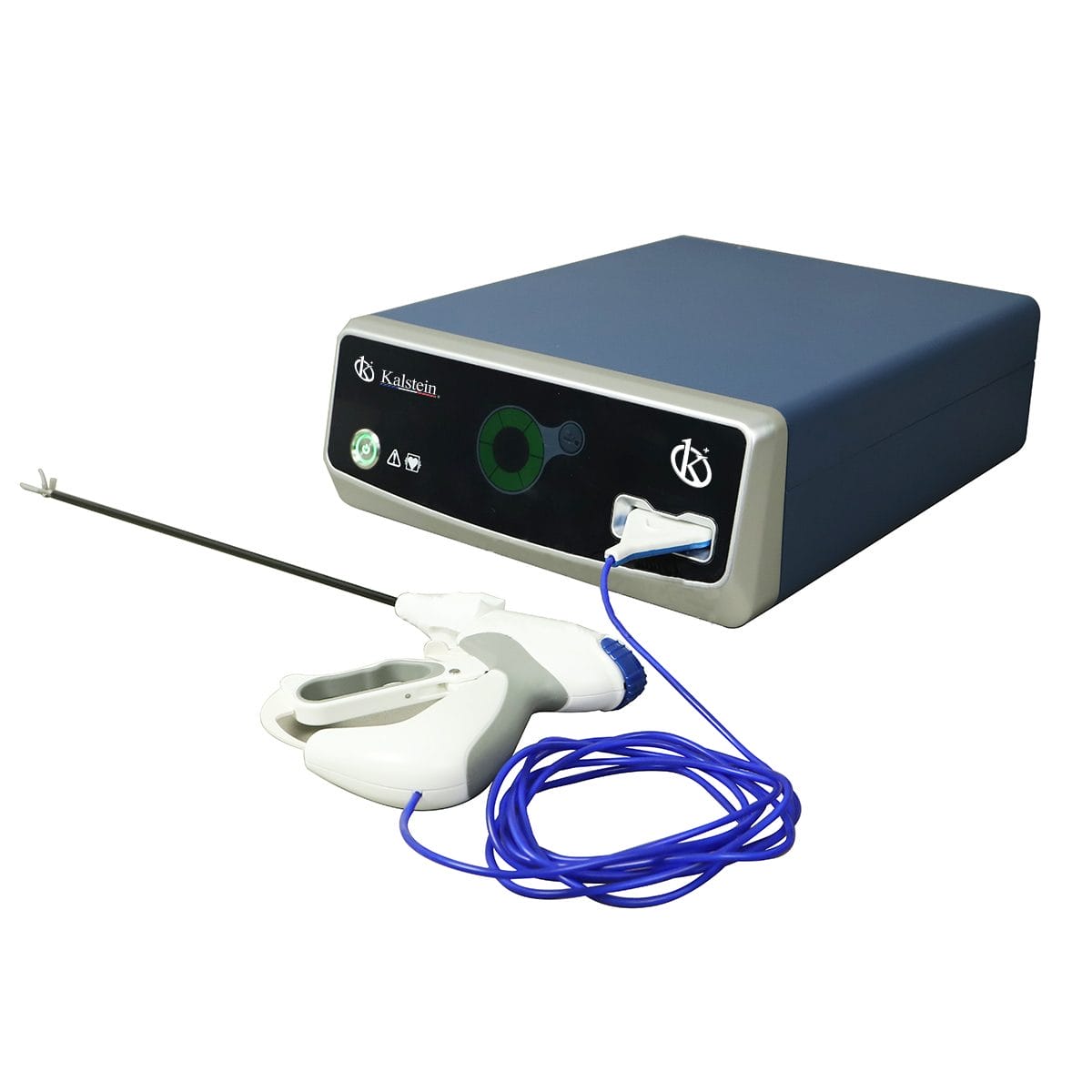

Thanks to its commitment to quality and innovation, Kalstein has significantly distinguished itself as one of the leading manufacturing companies of veterinary surgical equipment. Based on their extensive knowledge and experience, Kalstein has created a range of cost-effective and efficient products that are suitable for a wide range of animal medical procedures
Maximizing Laboratory Efficiency with Reactive Compounds
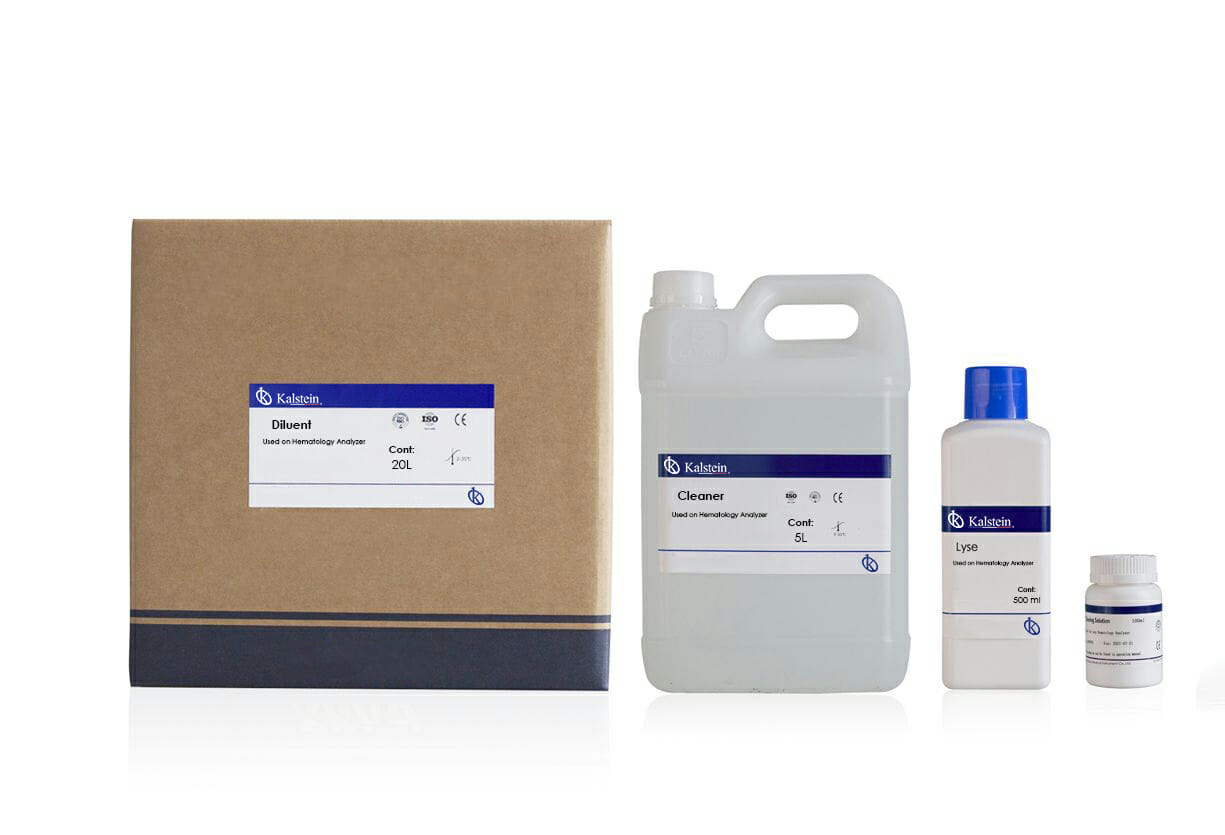

In the competitive world of science, optimizing lab performance has become a critical priority. Reactive compounds play a significant role in this regard, offering a range of advantages in the scientific field. This article will focus on discussing how these compounds contribute to improving laboratory efficiency, with details on the manufacturer Kalstein and factors associated with the price, purchase, and sale of these compounds.
Transcending Borders in Vascular Medicine: The Brilliance of the Eco-Doppler Scanner
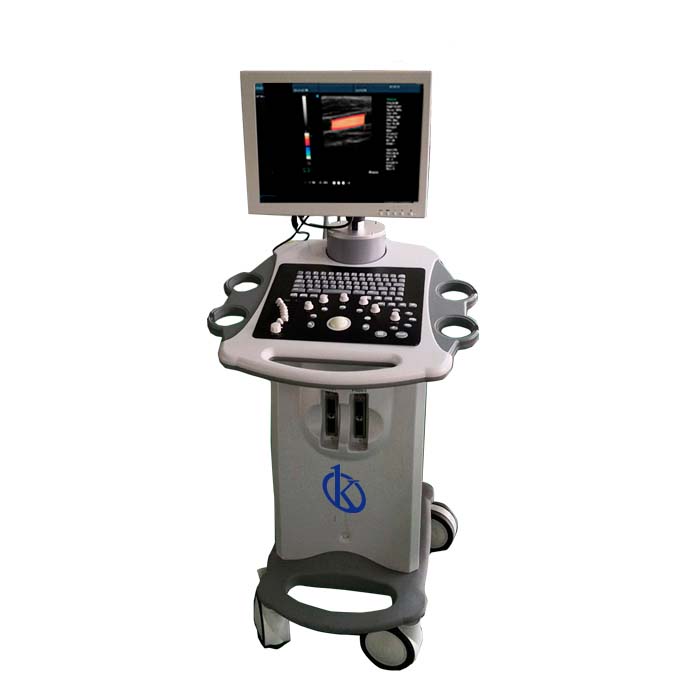
Vascular medicine has been radically transformed with the arrival of innovative technologies. Among the multitude of available equipment, the Eco-Doppler scanner stands out, a star product of the manufacturer Kalstein. This machine, designed to examine in detail the arteries and veins of the body, has expanded the horizons of vascular medicine by offering more precise and less invasive forms of diagnosis and monitoring.
Choosing Kalstein: An Integral Guide for Acquiring High-Quality Veterinary Radiography Equipment

Choosing a manufacturer to buy veterinary radiography equipment can be a daunting task. However, the answer is simple: Kalstein. As one of the leading manufacturers in the laboratory equipment market, Kalstein stands out for its specialization in combining high technology with versatile and functional designs. Buying veterinary radiography equipment from Kalstein guarantees experimental tools of high durability and precision.
Innovation and Quality in Veterinary Radiography Equipment: Kalstein’s Commitment

Veterinary radiography is a crucial diagnostic tool in pet medicine, providing detailed images of internal organs, bones, and tissues. This technology can be instrumental in detecting a variety of medical conditions, from heart diseases to bone fractures. However, the quality of veterinary radiography equipment can dramatically vary from one manufacturer to another. This is where Kalstein steps in, offering high-quality solutions at a competitive price.
Maximizing Veterinary Radiography Efficiency with Kalstein’s Superior Solutions
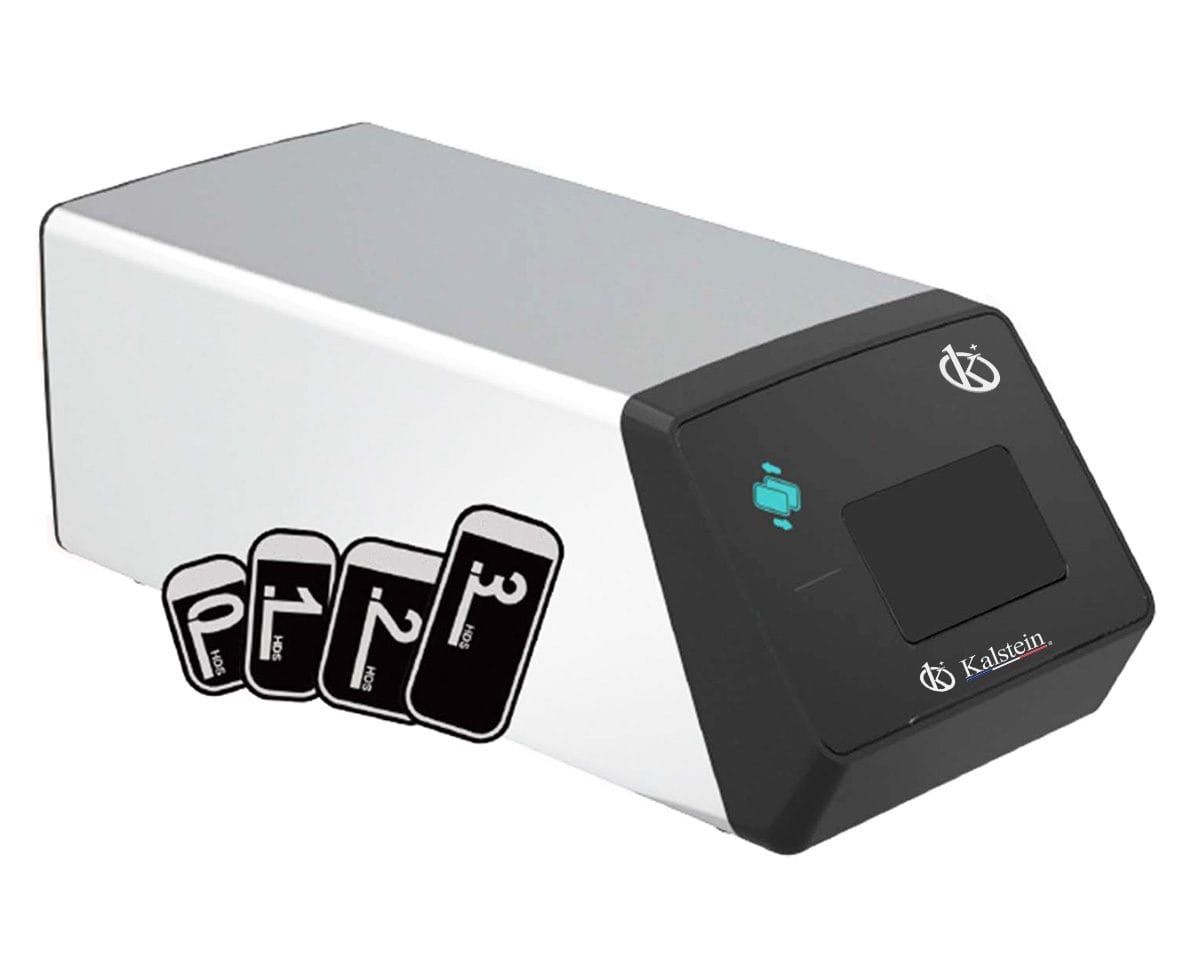

The world of veterinary medicine has greatly benefited from technology and innovation. The use of radiography equipment has become one of the pillars to ensure excellent care for our animals. As a leading manufacturer in the market, Kalstein offers its customers the best technology in veterinary radiography equipment. With equipment created thinking of the most demanding needs, Kalstein distances itself from its competition through the superiority of its products.
Trends in the Evolution and Use of Veterinary Radiography Equipment: Advantages of Choosing Kalstein
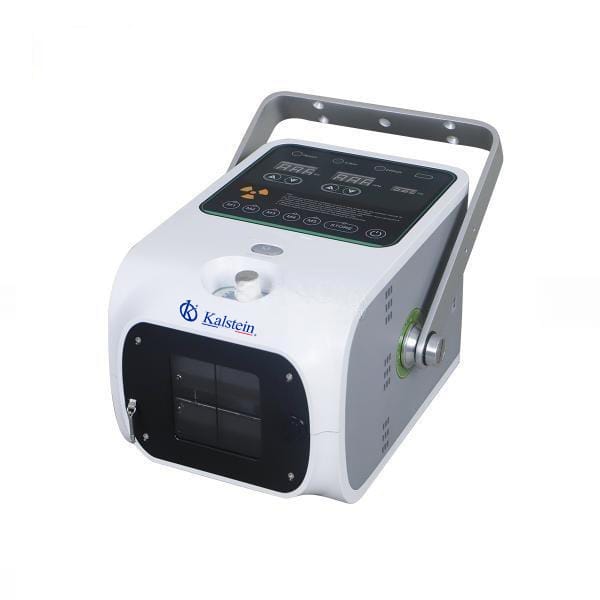

Radiography is an indispensable tool in veterinary medicine, providing accurate and efficient diagnoses for a wide variety of pets and animals of different species. However, the quality of the results largely depends on the quality of the radiography equipment used. As a leading manufacturer, Kalstein offers high-quality and cost-effective radiography equipment that meets the most demanding diagnostic needs.
